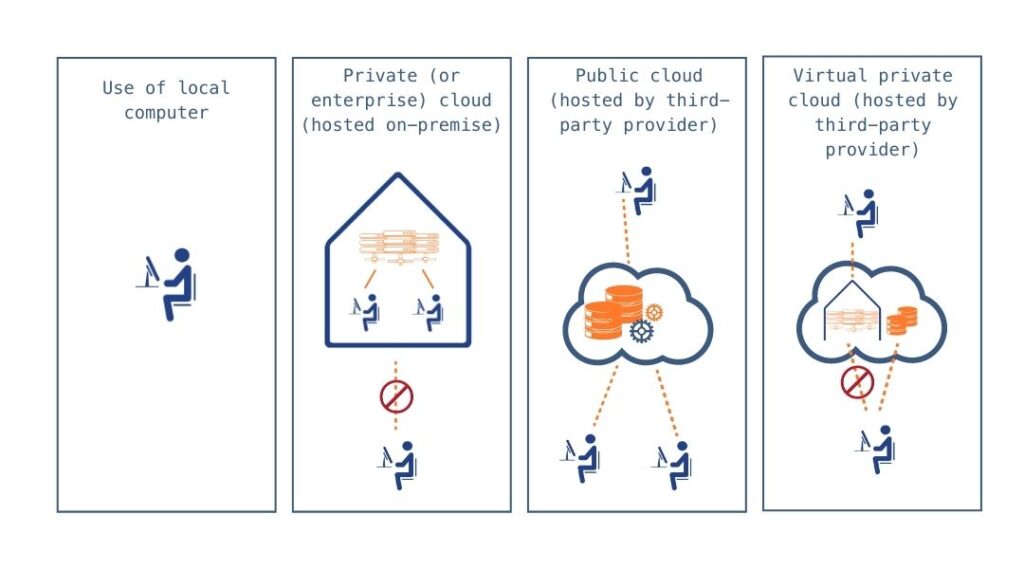
With a cloud or also with the Cloud computing is the internet-based provision of computing power, storage space or application software in the form of a service. The use of these infrastructure options mainly takes place via programmes by the devices accessing the storage spaces (here we also speak of clients) and via the existing web browser.
The principle of online storage
Since the mid-1990s as well as during the 2000s, a large number of companies have engaged in renting individual storage space in large IT data centres there and also managing it themselves. This storage space was then connected to the internet with the leased lines that were also rented.
The problem back then, however, was and is the corresponding maintenance of the components of these systems. This has repeatedly resulted in a total failure of the website or the workstation computers during the respective maintenance at the companies.
In 2006, Amazon, as an online bookseller, began renting storage and computing capacities to companies. This led to the creation of the Amazon Web Service, the cloud as a rentable information storage facility for the internet.
Due to the increasing number of services offered in the cloud, companies are increasingly outsourcing problems such as failure safety and data connection to third-party providers. The data available there can then be redundant (i.e. stored multiple times) at several locations.
This means that the accessing devices, such as PCs, smartphones or laptops and tablets, basically only need an internet connection and the access data assigned to them in order to access these online storages regardless of location (i.e. from anywhere in the world).
Such online storage is therefore already worthwhile for companies from the time when data from the company is available on more than just one computer. This is especially true when mobile devices, such as tablets or smartphones, are used in the workplace on a daily basis in addition to PCs.